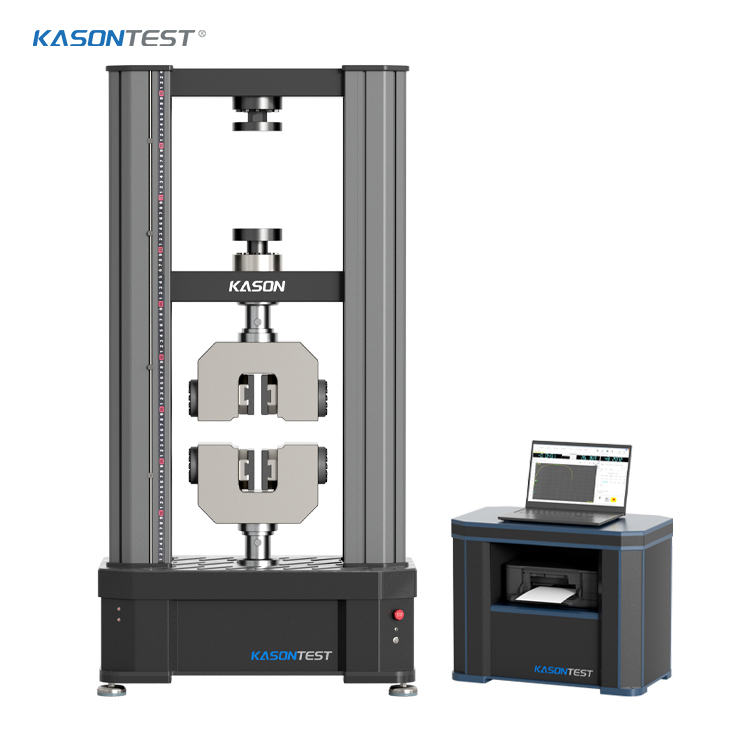
Sample Testing
Sample testing is integral to broader materials testing (as outlined in the introduction to materials testing). It ensures that the materials evaluated in labs are truly representative of what will be used in production. For example:
When testing the compressive strength of concrete, samples (cylinders) are cast from the same mix used in a building and tested to ensure the structure will be safe.In polymer manufacturing, samples from each batch are tested for flexibility to confirm they meet the requirements of a product like a plastic pipe.
Without reliable sample testing, materials testing results could misrepresent the actual performance of the material in real-world applications.
Applications Across Industries
Sample testing is universal across sectors:
Manufacturing: Testing samples from production lines to ensure consistency (e.g., checking the thickness of aluminum sheets).
Pharmaceuticals: Analyzing samples of drugs to verify purity, dosage, and stability before releasing a batch.
Food Safety: Testing food samples for contaminants, pathogens, or nutritional content to comply with health regulations.
Construction: Evaluating samples of bricks, cement, or steel to confirm they meet structural standards.
Aerospace: Testing samples of alloys or composites to ensure they can withstand extreme conditions before using them in aircraft.