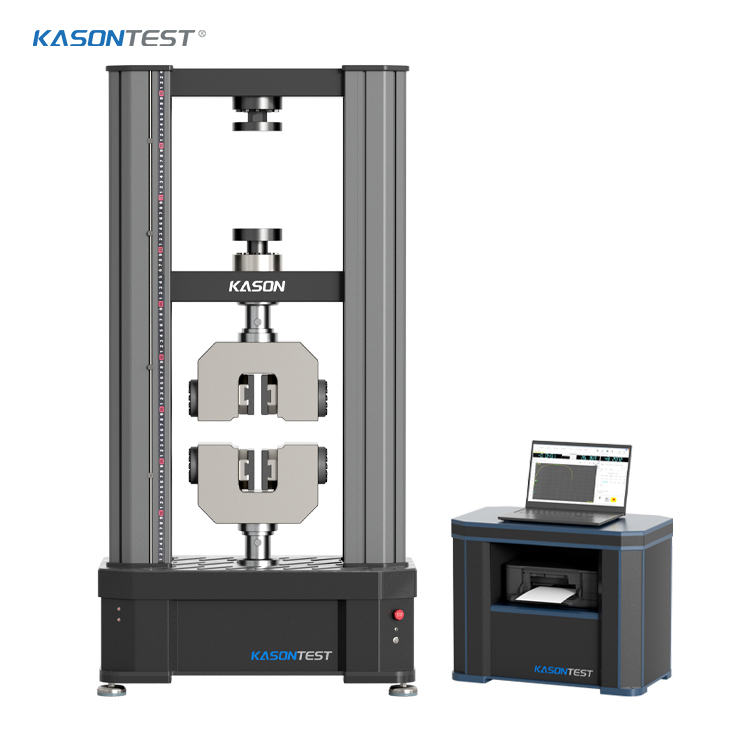
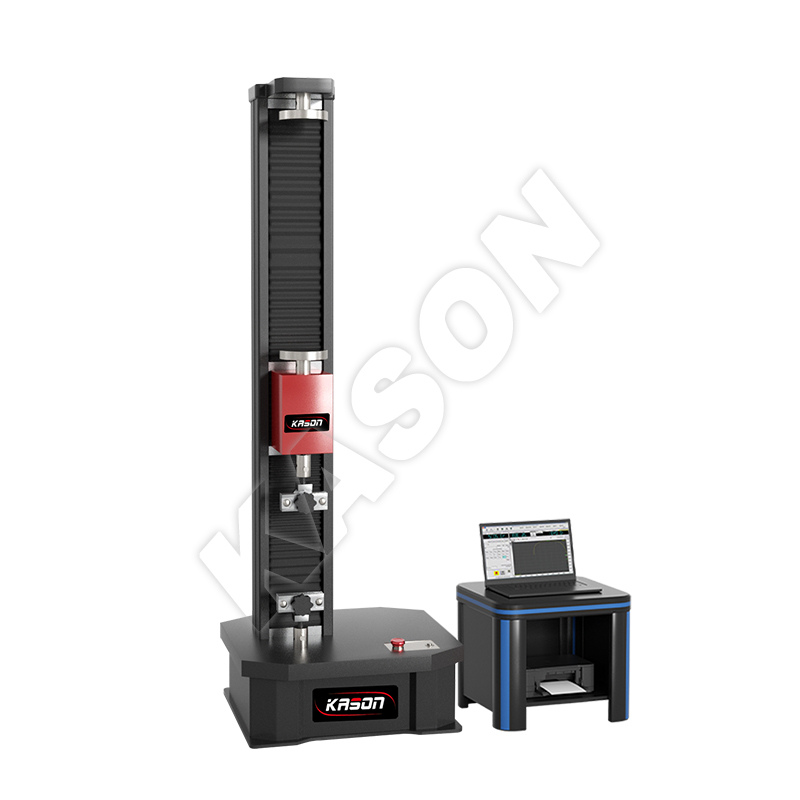
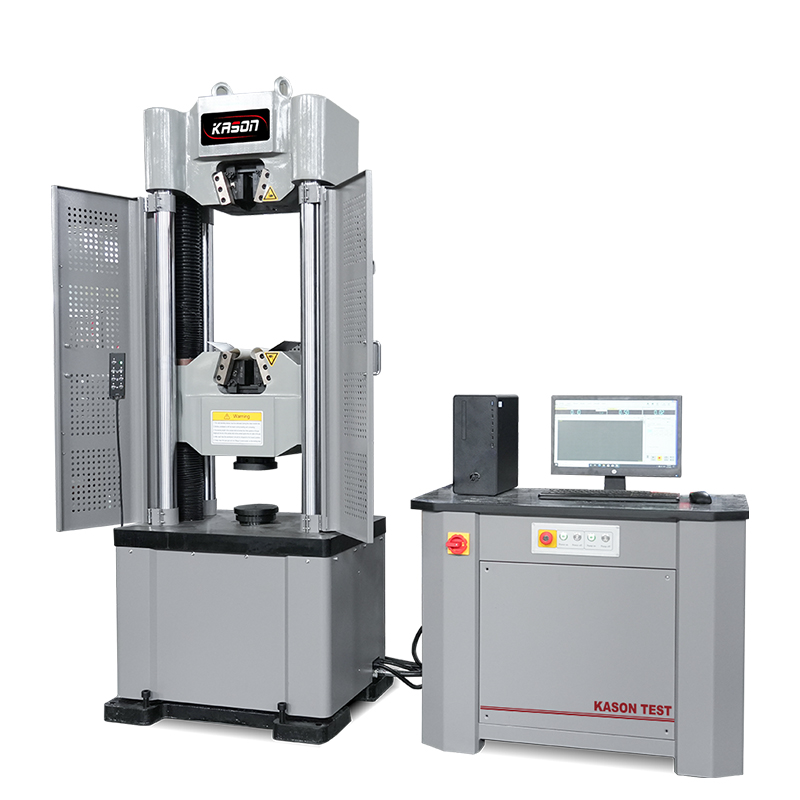
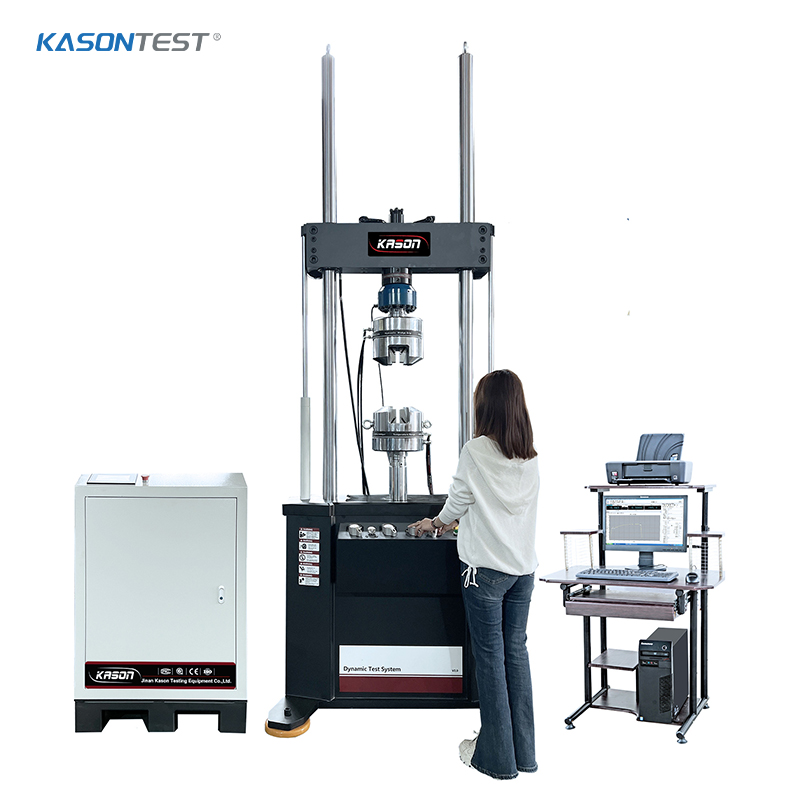
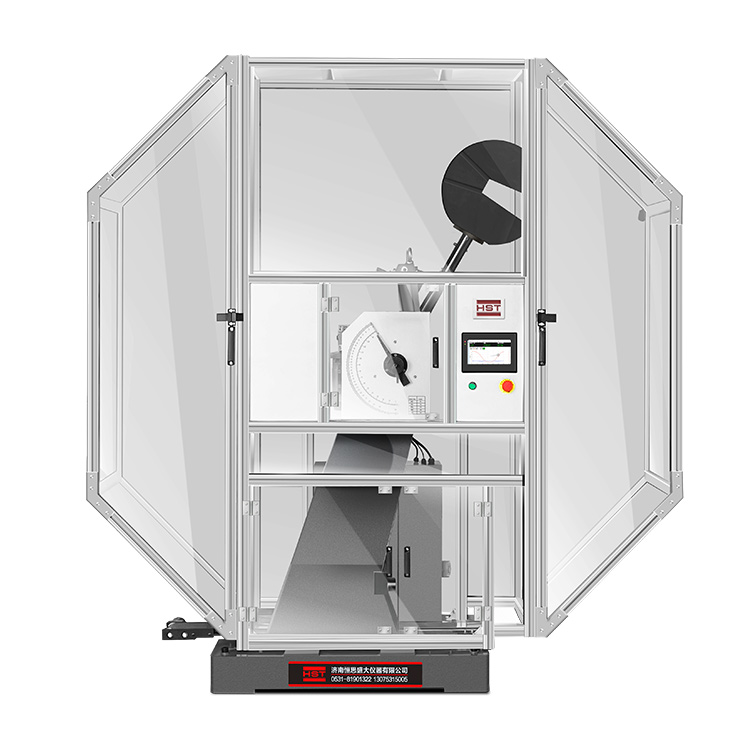
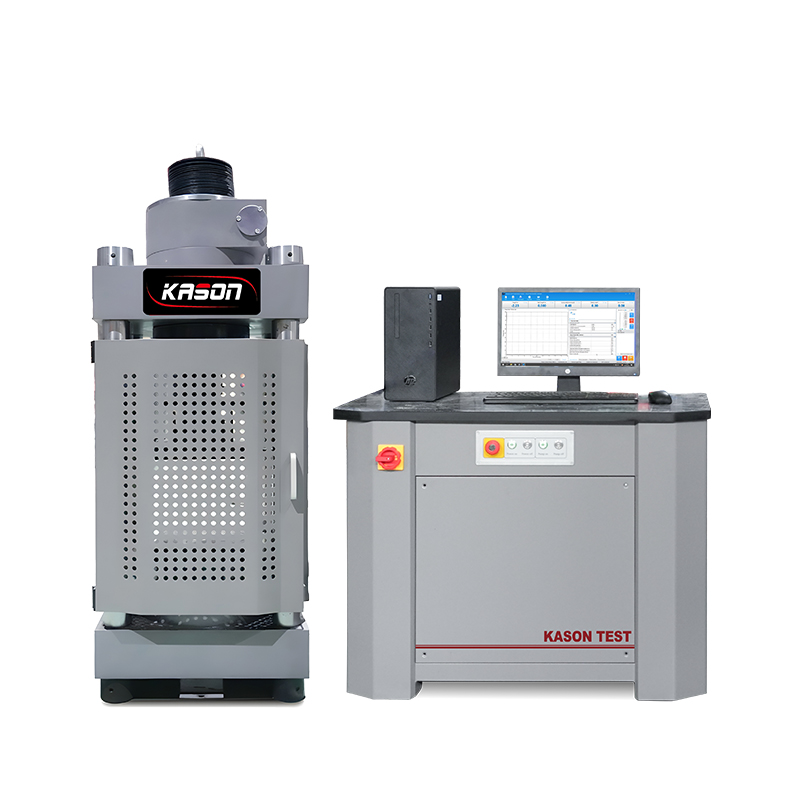
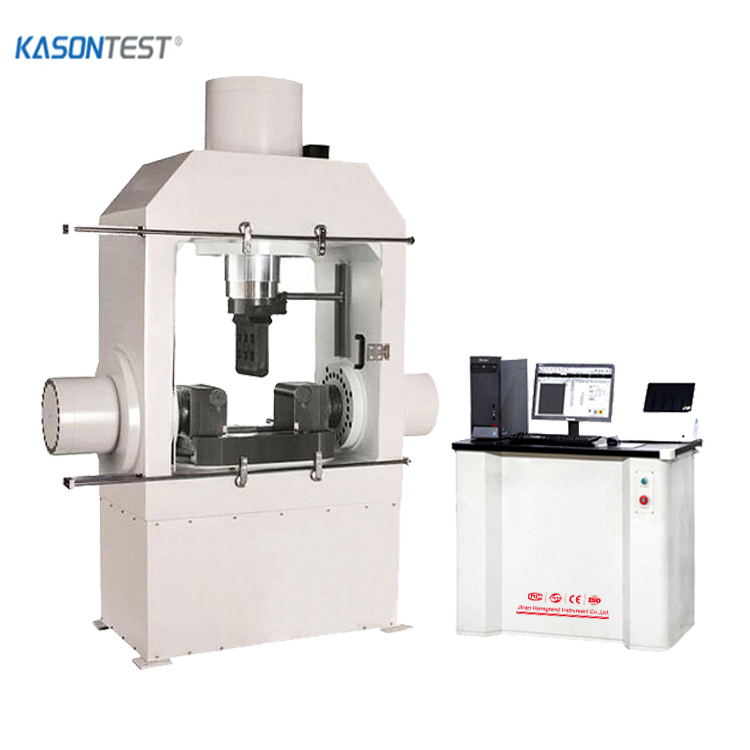
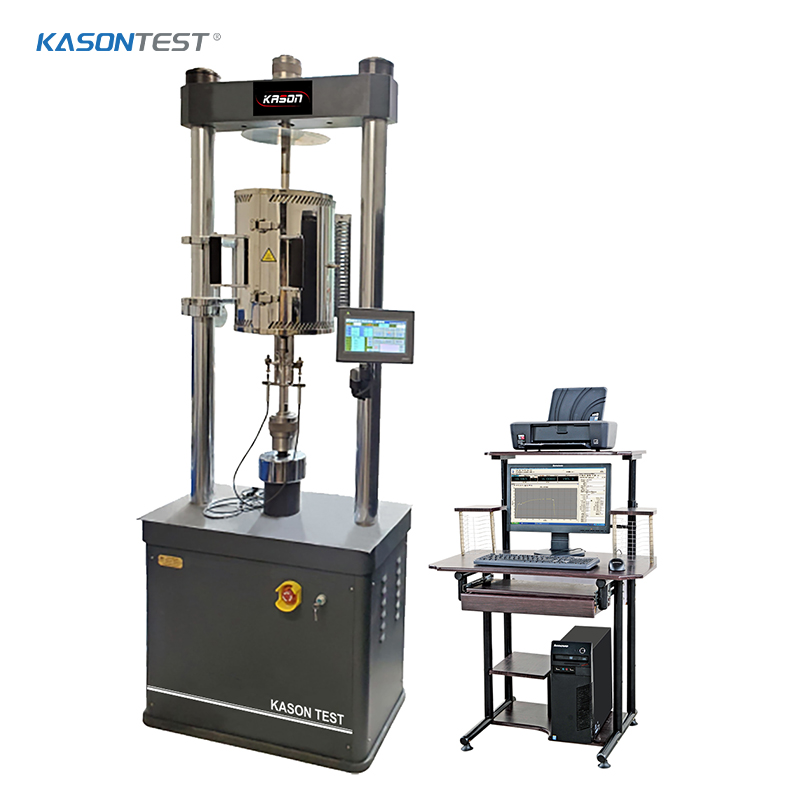
Rockwell hardness test to ISO 6508 / ASTM E18
The Rockwell hardness test is a hardness test based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters. The result is a dimensionless number noted as HRA, HRB, HRC, etc., where the last letter is the respective Rockwell scale. Larger numbers correspond to harder materials.




In the Rockwell hardness test, a differential-depth method, the residual depth of the indent made by the indenter, is measured. In contrast, the size of the indentation is measured in the Brinell, Vickers and Knoop optical test methods.
The deeper a defined indenter penetrates the surface of a specimen with a specified test load, the softer the material that is being tested. The Rockwell hardness (HR) is then determined from the residual indentation depth, along with a few other factors.
In hardness testing according to Rockwell, the total test force is applied in two steps. This is intended to eliminate effects from the roughness of the specimen surface (e.g., grooves on the specimen) as well as measurement errors caused by the play of the indentation depth measurement.