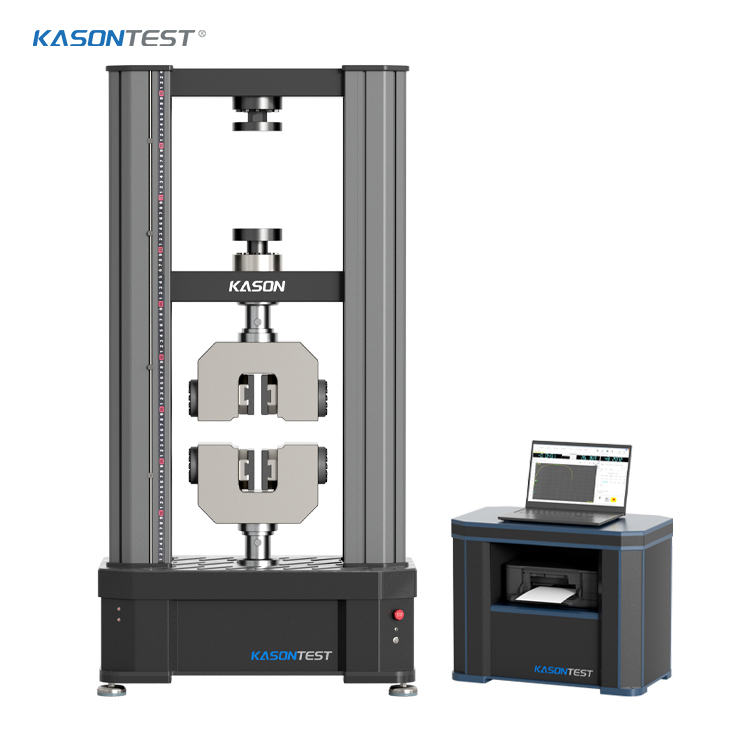
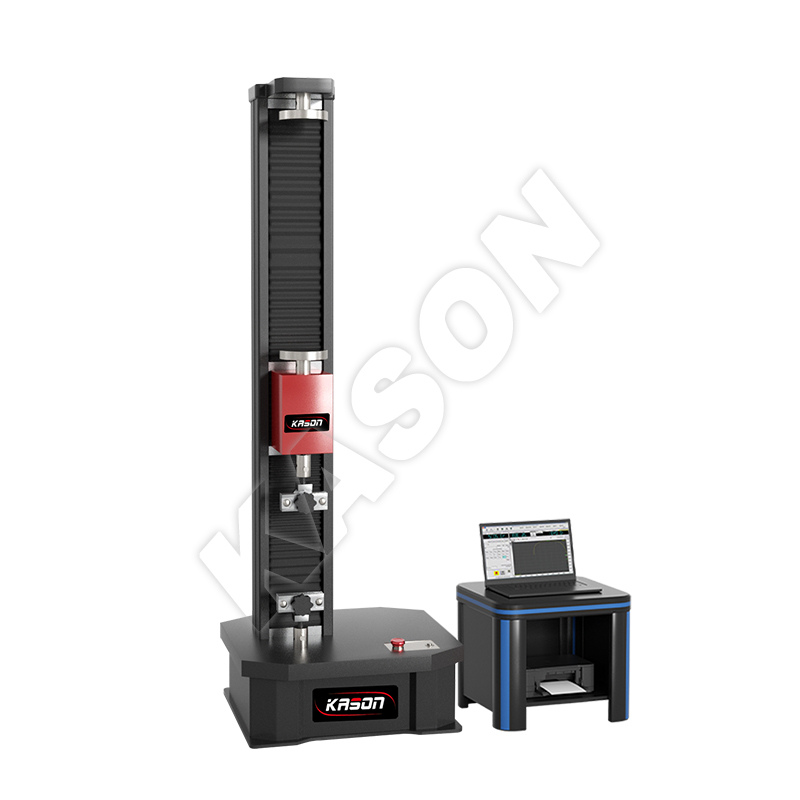
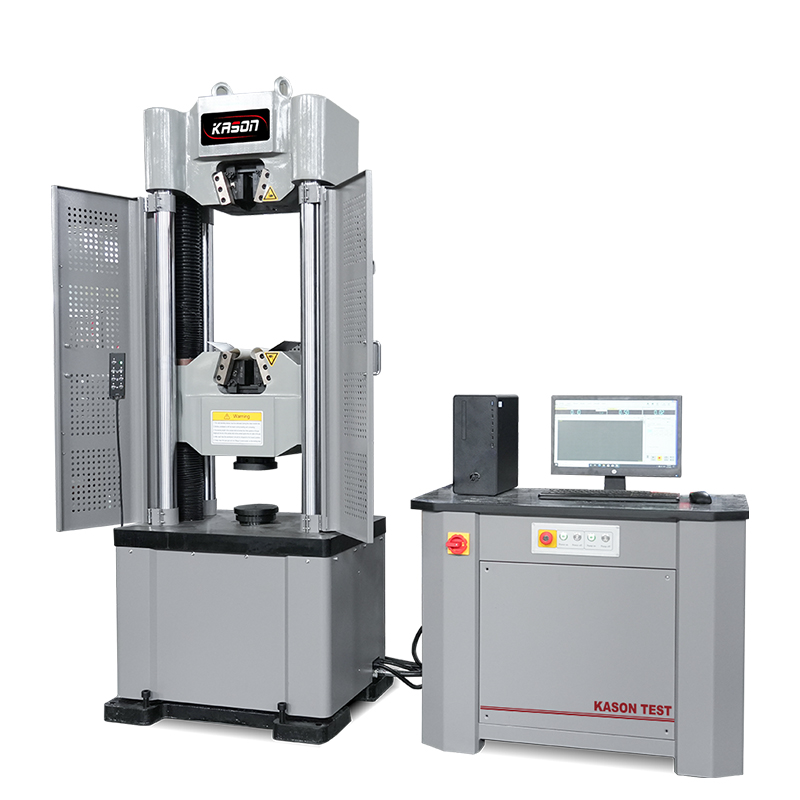
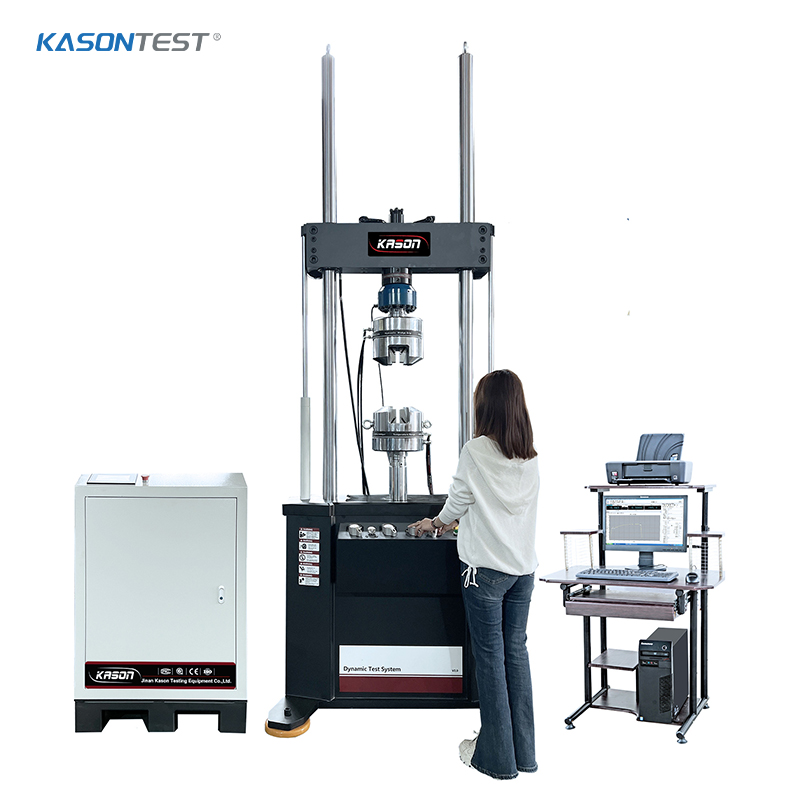
Pharmaceutical tablets and capsules are commonly packaged in blister packs that protect the enclosed tablets and capsules from moisture and contamination. This optimizes the product stability and maximizes its shelf life. The two primary components of a blister pack are the rows of cavities, typically made of thermoplastic, and the lidding seals that can be made of paperboard, aluminum, or plastic. However, in pharmaceutical packages, aluminum foil is most frequently used. It is important for manufacturers to ensure that the blister pack does not break too easily, yet it needs to be brittle enough to allow consumers to break by hand in order to dispense the tablets or capsules. Many pharmaceutical companies utilize a variety of blister pack sizes to accommodate various pill diameters, which poses a challenge for testing.