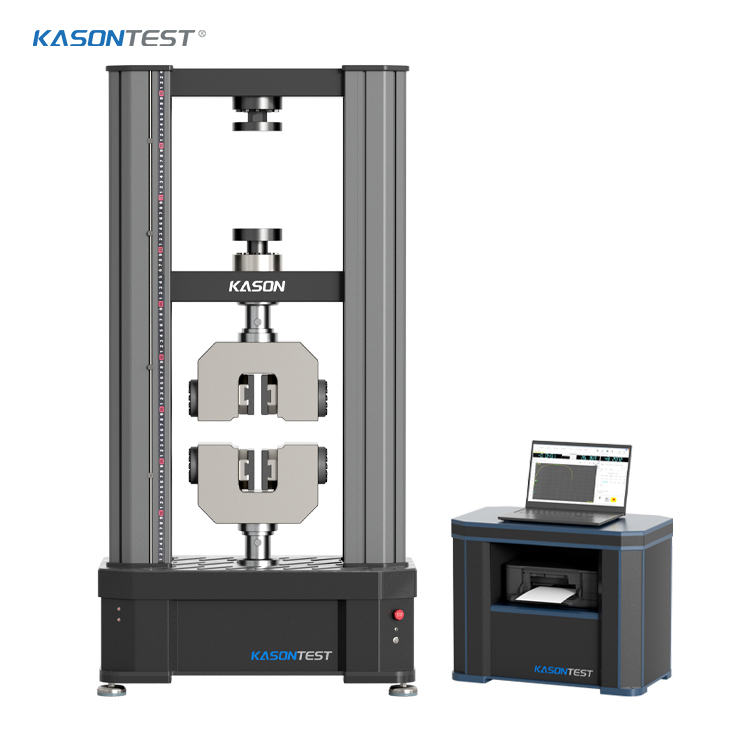
ASTM F2516 Tensile Testing of Nitinol Wire
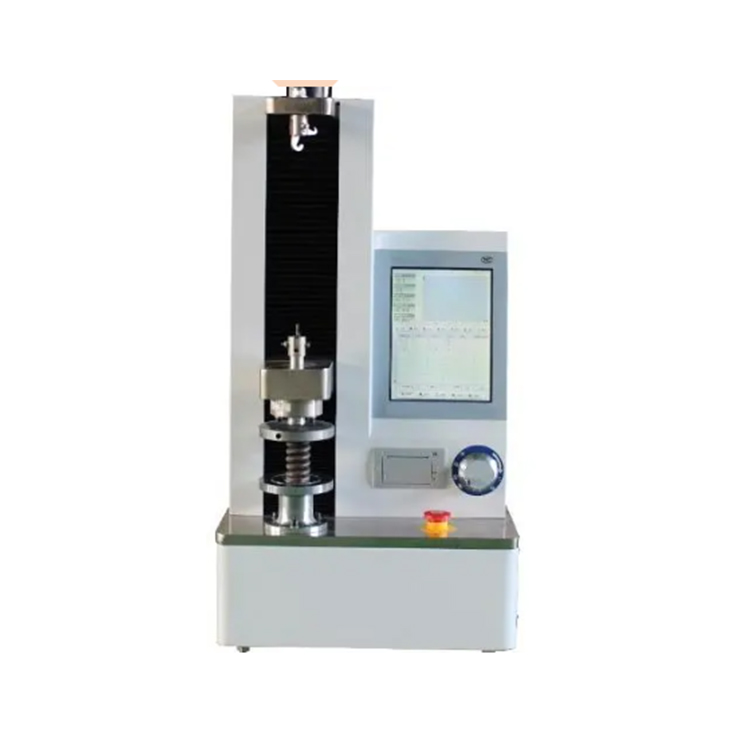
ASTM F2516 measures the tensile properties of superelastic nickel-titanium or Nitinol. The material properties of nitinol are different from those of most other materials – nitinol will change its structure depending on its temperature or the amount of stress applied to it. This means that it will exhibit very different stress strain profiles during loading and unloading, which is why this standard captures both an upper and lower plateau strength, rather than a singular yield strength. The ASTM F2516 test method is designed to pull the material in tension to 6% strain, then unload the material to a value of less than 7MPa before being pulling it to failure.Standard At A Glance
Materials:Metals, Biomedical
Test Types : Tension,Compression
Standard: ASTM F2516
What is Nitinol Used For?
Nitinol's unique properties mean that it is used extensively in the biomedical industry to create stents, dental wires, catheter guidewires, internal fracture fixation devices, and biopsy forceps. One of its properties - shape memory - enables it to "remember" its shape when formed at a certain temperature. When the temperature is lowered beyond this point Nitinol can be molded to any other shape, but will automatically revert to its original shape once it reaches the temperature at which it was initially formed. This property makes it extremely useful for the creation of stents, which are used to hold open blood vessels and prevent severe clots. The stent can be transported through the body to the target location in a compacted form, reforming to its original cylindrical form once it warms up to body temperature at the target location. Nitinol is also commonly used for braces – the Nitinol is molded into the desired final shape, and the temperature within the mouth stresses the material to reform, slowly adjusting the teeth into their ideal positions. Unlike more traditional braces, nitinol braces wire is especially beneficial because it does not require frequent retightening.