Chemical
The chemical industry is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, encompassing the production, processing, and distribution of chemicals and chemical-based products that enable countless sectors of the global economy. This vast industry transforms raw materials into a diverse range of substances, from basic chemicals to specialized compounds, serving as a critical link in supply chains for agriculture, healthcare, construction, and consumer goods.At its core, the chemical industry operates through complex processes that convert raw materials such as petroleum, natural gas, minerals, and biomass into useful chemicals. The sector is broadly categorized into basic chemicals (including petrochemicals, industrial gases, and inorganic chemicals), specialty chemicals (adhesives, catalysts, and surfactants), and consumer chemicals (household cleaning products, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals). Each category serves distinct markets with unique production requirements and quality standards.
Global chemical production exceeds $5 trillion annually, with Asia-Pacific dominating as the largest regional market, led by China, which accounts for over 40% of global chemical output. Europe and North America focus on high-value specialty chemicals and pharmaceutical products, while emerging economies in Latin America and Africa are rapidly expanding their chemical manufacturing capabilities to meet growing domestic demand.
The industry’s applications are virtually ubiquitous. In agriculture, fertilizers and pesticides enhance crop yields, ensuring global food security. The healthcare sector relies on chemicals for pharmaceutical ingredients, medical devices, and diagnostic tools. Construction benefits from plastics, adhesives, and coatings that improve building durability and energy efficiency. Transportation depends on high-performance materials like lightweight polymers and advanced fuels, while consumer goods ranging from textiles to electronics incorporate various chemical components.
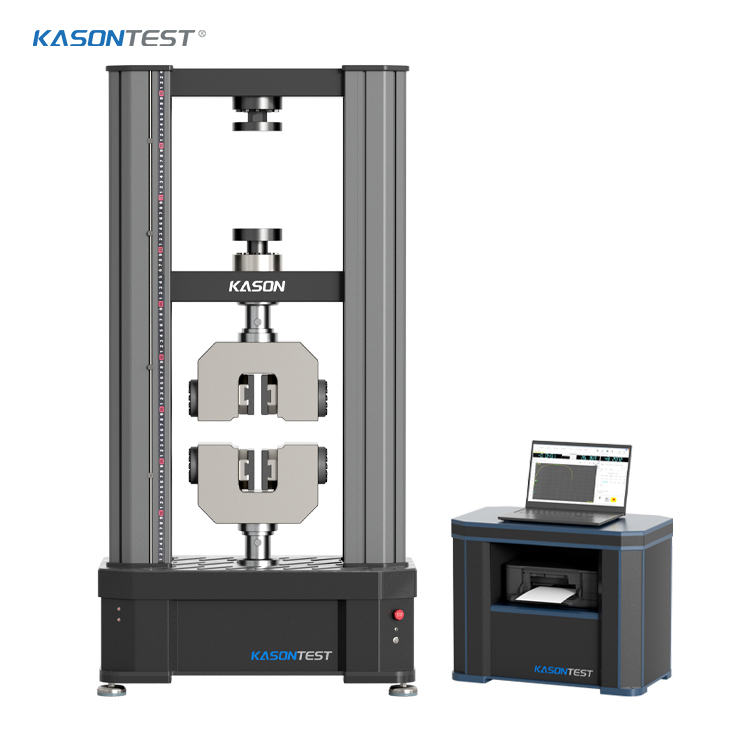
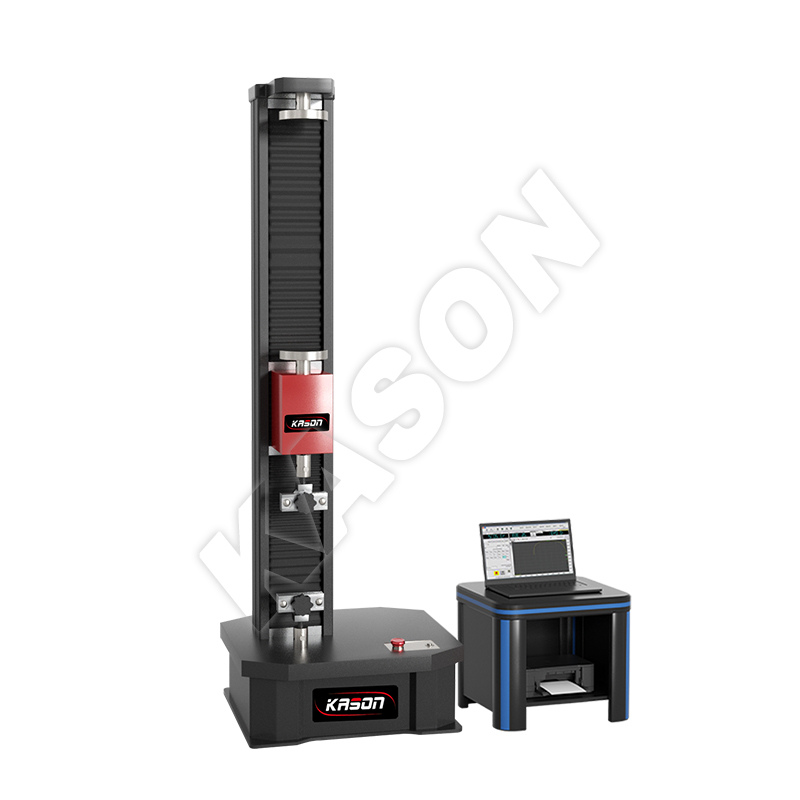
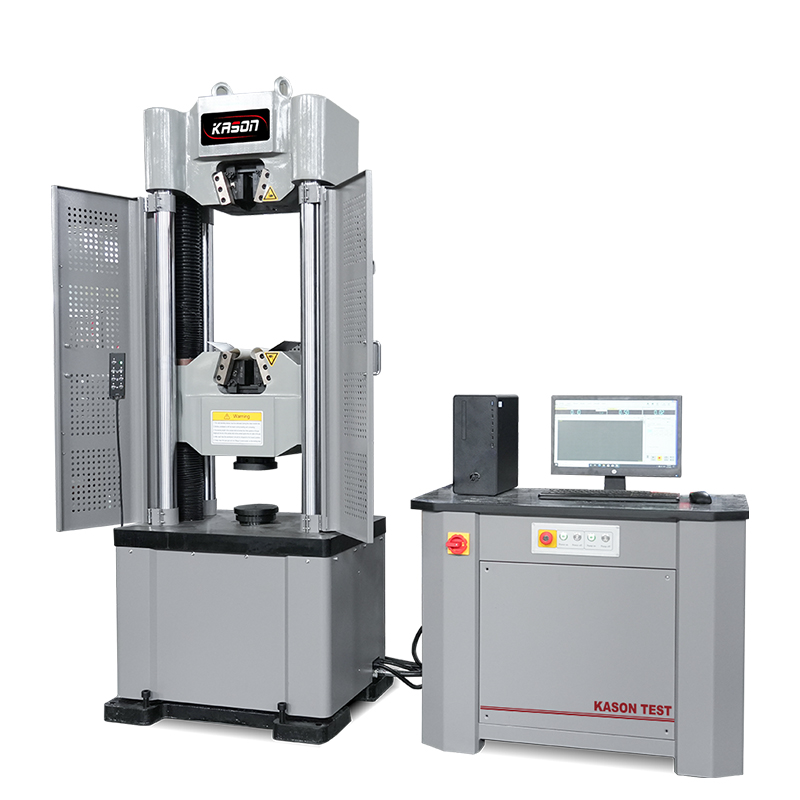
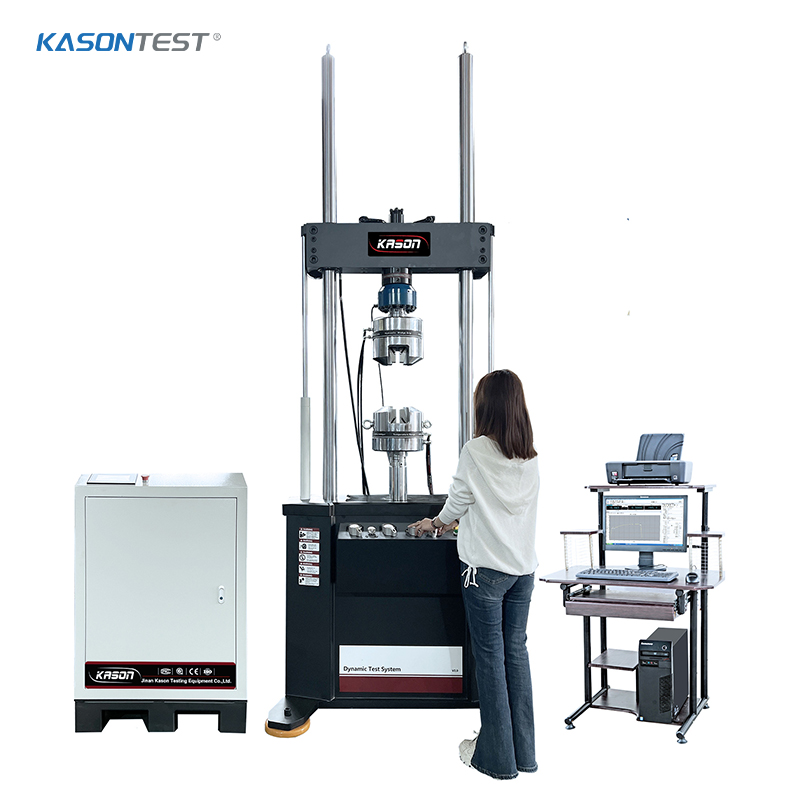
Chemical manufacturing involves sophisticated processes including synthesis, distillation, polymerization, and catalysis, often requiring precise control of temperature, pressure, and reaction conditions. Recent technological advancements have introduced automation, artificial intelligence, and digital monitoring systems to optimize production efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance safety protocols.
Sustainability has become a central focus, addressing environmental concerns such as carbon emissions, waste management, and resource depletion. The industry is increasingly adopting green chemistry principles, developing bio-based feedstocks, and implementing circular economy practices to recycle chemical waste. Companies are investing in carbon capture technologies and renewable energy integration to reduce their environmental footprint.
Key challenges include navigating complex regulatory frameworks, ensuring safe handling of hazardous materials, and adapting to volatile raw material prices. However, ongoing innovation in materials science and process engineering continues to drive the development of more sustainable, high-performance chemicals, solidifying the industry’s role as a driver of technological progress and economic growth.